Vacuum Forming Introduction
A detailed explanation of vacuum forming is provided in this article. The following topics will be covered:
-
Vacuum forming – what is it?
-
Vacuum forming materials
-
Machines used for vacuum forming
-
Vacuum forming products
-
Cons and pros of vacuum forming
-
More to come
Chapter 1: Vacuum forming – what is it?
A vacuum former uses a vacuum to shape and heat plastic material.
From small objects to huge industrial machinery, vacuum forming is one of the oldest and cheapest methods of plastic molding. The low cost, efficiency, speed of imitation, and ease of use of vacuum forming make it a popular technique for making molds for smaller objects. A vacuum forming process involves placing a layer of plastic on a mold, and then applying a suction force to shape the plastic into the desired shape. Plastic thermoforming is also known as vacuum forming because only a mold is needed, and the plastic is placed over it.
Vacuum forming uses two types of molds:
-
Male mold or positive mold
-
Female mold or negative mold
The male mold or positive mold is a convex-shaped one. The plastic is placed on the outer layer of the mold, which helps contour the inner dimensions, while the female or negative mold is concave. In order to contour the outside dimensions of the plastic accurately, it is placed inside a mold.
Vacuum forming is the simplest of all forms. Even so, advanced technology such as heat, hydraulic and pneumatic controls are being introduced to produce more precise and desirable products at a reasonable pace. Bath and shower trays, vehicle parts, refrigerator liners, plastic storage boxes, etc., are among the products made by vacuum forming.
What is the difference between a thermoforming process, a vacuum forming process, and a pressure forming process?
In thermoforming, plastic sheets are heated to become flexible and then contoured in molds and trimmed. Thermoforming can be divided into two types:
-
Vacuum forming
-
Pressure forming
Their main difference is the number of molds used in manufacturing their products.
Using a vacuum pump and a mold, vacuum forming is performed. Using a vacuum, the heated sheet is placed into the mold of the desired shape. The material is mainly used in contoured packaging for food and electronics. Two molds are used for pressure forming at the same time. The sheet is placed inside one mold and the other mold is placed on it rather than using suction from the vacuum pump. A precise and aesthetically pleasing mold, such as one for appliances, can be produced using this process. Furthermore, pressure forming is ideal for forming parts that need to be formed evenly and that go deeper into molds.
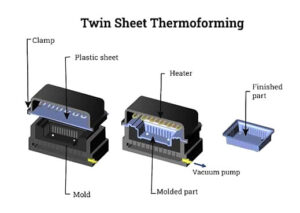
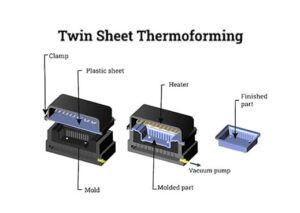
Twin Sheet Thermoforming
The twin sheet thermoforming process is done either by pressure forming or vacuum forming, but with the help of two molds. By compressing two plastic sheets simultaneously, one on the top platen and the other on the bottom platen, two plastic sheets are created. As soon as the sheets were formed, they remained in the vacuum at their melting temperature. The two platens are compressed and joined together to form one product. Products with hollow structures are formed using twin sheet thermoforming. As shown in the figure below, twin sheet thermoforming involves the following steps:
There are advantages to this process over other processes.
These include:
-
Tooling costs are about 20-30% lower than other processes.
-
An enclosed cavity is allowed.
-
Twin sheet thermoforming produces products that are more rigid and stable than thin-walled thermoforming.
-
Reinforcements can be added internally during this process.
Many transportation products are made with twin sheet thermoforming, including pallets, portable toilets, toys, fuel tanks, marine products, doors, ventilation ducts, surfboards, spine boards, and many others.
The materials used in vacuum forming
A variety of thermoplastics can be used in vacuum forming, but the most common ones are as follows:
Polycarbonate (PC)
Many machine parts are made from polycarbonate (PC). It is a good choice as it is virtually unbreakable, highly resistant, UV-protected from one or both sides, and half the weight of glass; therefore, they are easy to handle and install. Skylights, aircraft trim, and light diffusers use it.
Polystyrene (PS)
In many formulations, polystyrene (PS) is the most versatile thermoplastic. Unmodified polystyrene is moderately intense, precise, brittle, and rigid. Additionally, it has good electrical properties, dimensional stability, low cost, versatility, and is easy to process. Thus, it is widely used in food packaging, disposable cups, and plates.
Polypropylene (PP)
The polymer polypropylene (PP) is also a plastic. In schools and offices, it is used for model making, crafts, and report covers as a material for vacuum forming. A semi-rigid sheet with high heat, fatigue, and chemical resistance, these sheets are inflexible and semi-rigid. Additionally, they are crystalline, non-polar, and translucent.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride is readily available and widely used. Compared to all other plastic polymers, it has excellent tensile strength, rigidity, and density. Furthermore, it is eco-friendly and chemically resistant. It is primarily used for commercial printing, laminations, and vinyl lettering.
Polyethylene (PE)
The polyethylene sheet is made from petroleum, and it is highly resistant to chemicals and water. It is very stable in cryogenic environments, has a low coefficient of resistance, and is highly malleable. Low cost and suitability for almost all environments make it widely used.
Polyester Copolymer PETG
An unmodified thermosetting plastic with high durability, strength, and resistance to harsh environments. In vacuum forming, it is used because it can be easily molded, dyed, and formed.
Acrylic PMMA
Acrylic PMMA is a widely used plastic sheet that is affordable, transparent, easy to mold, and more resilient than expensive glass. Cars, windows, smartphone screens, and even aquariums use it.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene ABS
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a thermoplastic that resists chemicals, impacts, abrasions, and stress. In addition to being rigid, hard, and stable, it also has good electrical properties. Among its uses are rigid pipes, automobile parts, and car wheels.
Chapter 2: Vacuum forming machines
Although vacuum forming machines work on the same formula, some machines operate differently depending on their capabilities. There are four types of vacuum forming machines:
DIY Machine
For smaller-scale production, DIY machines are used. There are quite a few heaters in it. As a result, they cannot be used in industrial production. DIY machines might use ceramic heaters, but they are not specialized enough to use complex tools such as plugs due to their slow response times. Simple in structure, these machines are easy to maintain, install, and handle. There are three separate heating zones with different temperature controls in the single working station. The heating box is protected with a lid, and a vacuum pump is located at the bottom of the machine. Toys, masks, stationery, tableware, tools, blister packs, cosmetics, and more can be made by DIY machines.
Table Top Machine
Acrylic products are formed using a tabletop vacuum forming machine. There are three different series of these machines, each with a different function. The operating system is similar to that of other vacuum forming machines; suitable materials include acrylic, ABS, PC, PS, PVC, PP, and others. Automobiles, aerospace, signs and displays, and film and design sets use these.
Single Heater Machine
The single heater machine can be used for various plastic sheets, including starch degradation sheet, optical degradation sheet, green sheet APET, PETG, and various color sheets, such as HIPS, PVC, PET, PS, PP, etc. The machines are mechanically and electrically integrated with automatic temperature controllers, high frequency, and efficient temperature gain. There are ten stalls in furnaces for gear switches, easy to install, and automatic temperature controllers. The machine produces thin-walled food containers, travel goods, textiles, cosmetics, decorations, medical supplies, toys, and electrical goods.
Double Heater Machine
Electrical-mechanical integration is used in a double heater vacuum forming machine. Featuring all digital power controls, it can perform all feeding, heating, forming, cooling, trimming, and finishing functions. It is applied to plastic sheets such as PS, HIPS, PVC, PET, and PP. A sheet feeding frame that automatically feeds sheets ensures correct sheet feeding and saves staff time. 60 infrared ceramic bricks make up this machine’s heaters, and each brick contains a self-regulating element to regulate the sheet’s temperature. Adapted to negative molds, the double heater machine can also make concave or convex molds according to requirements. The spray mists are there to cool down the heated sheet with regulators that control the amount of water sprayed. With the double heater machine, you can make trays, medical trays, telephones, cookies, hardware, tableware, and plastic packaging.
Process of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming have numbers of steps and contribute to the efficient and effective molding of plastic. As a result, this chapter provides a step-by-step description of the process.
Clamping
For this purpose, the clamps of the machine should be strong enough to hold the plastic sheet firmly in place. A single heater can hold and form thick materials as thick as 6mm, while a twin heater can hold and form materials as thick as 10mm. To avoid any accidents, all moving parts in an automatic machine should be interlocked and guarded.
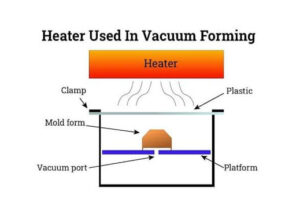
Heating
In the vacuum forming process, heaters consist of an infrared element enclosed within an aluminum reflector plate. In this process, any material can be used, but the important thing is that the sheet is heated evenly throughout its thickness. Every zone needs energy controllers to regulate an optimum temperature for the material for this purpose. Due to their high thermal mass, ceramics take a long time to heat up and therefore they take a long time to mold. Using a pyrometer can help determine the exact melting temperature of materials, and if it is connected to a temperature control system, it will be more feasible. It is recommended to use a twin quartz heater for thick sheets, as it helps to heat thicker materials evenly and penetrate thicker materials more efficiently. With these heating strategies, heat can be evenly penetrated with precision and at a low cost.
Sheet Level (Auto-Level)
Some machines do not have Sheet Leveling, which prevents plastic from sagging. The machine scans the heater and melted plastic sheet with a photoelectric beam. When the melted sheet sags down and the beam is broken, some air is injected into the sheet to lift it up and prevent it from sagging down again.
Pre-Stretch (Bubble)
In order to ensure even thickness on the entire surface of the plastic sheet when it is melted and ready to go in the mold, this step is done to stretch the plastic sheet. By using air pressure or vacuum plugs, plastic is pre-stretched to prevent any disfigurement.
Plug Assist
Following the stretching phase, a plug is used to assist. Plug-assisted vacuum forming is used when a normal vacuum forming machine fails to distribute the plastic sheet evenly on the mold. Filling all the vacant spaces in the molds is made easier with this plug which helps distribute the melted plastic sheet evenly throughout the mold surface. Furthermore, these plugs prevent the plastic sheet from thinning, allowing more material to reach the bottom of the mold.
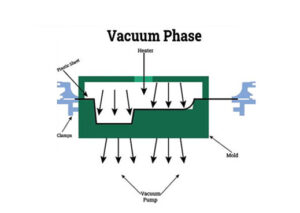
Vacuum
Stretching and plugging remove extra air from sheets and molds. To remove any air bubbles trapped between the plastic sheets and the molds, a van vacuum pump is placed in the machine. A vacuum pump of about 27″ mercury should be able to generate enough pressure. When dealing with larger machines, a vacuum reservoir along with a high volume vacuum pump is used to remove air particles rapidly before the plastic sheet cools down.
Cooling and Release
A cooling process is applied to the plastic form before it is released. Melted plastic needs time to settle, so cooling is necessary. It will be deformed otherwise. For cooling purposes, the machine is equipped with fans, which aid in the process. Along with fans, there are nozzles attached to the fans that spray chilled water directly on the plastic sheet, speeding up the cooling process by 30%. As these polymers exit the machine, temperature control units regulate the cooling temperature of the polymers in order to assist in the cooling process. Upon cooling down, the molded plastic sheet is released towards the next step.
Trimming and Finishing
After the plastic sheet is released from the machine, different types of trimmers are used to trim the molded sheet. The sheets are cut, drilled, or slotted according to the product’s requirements. The finishing process may include decoration, printing, or strengthening. The type of trimming available depends on many factors, such as the part size, the cut type, the thickness of the material, etc. Trimming thin gauge parts is usually done with a mechanical trim press, also known as a roller press.
Chapter 3: Vacuum forming products
The vacuum forming method is used to make hundreds of plastic products we use every day. In addition to medical products, vacuum forming is also used in industries, household items, automobiles, lawn and garden equipment, agricultural equipment, electronics, display centers, commercial equipment, fitness, and many more. Almost every vacuum-formed product will be covered in this topic.
Medical Equipment
Many types of medical equipment are made from plastic using the vacuum forming method. Such as thermoformed trays, blister packs, clamshells, CT scanner components, MRI machine components, X-ray machine components, carts, trays, heating pads, operation kits, vacuum formed trays, and many more. Some of them are shown below:
Medical Equipment
A variety of medical equipment is made from plastic using the vacuum forming method. A few examples are thermoformed trays, blister packs, clamshells, CT scanner components, MRI machine components, X-ray machine components, carts, trays, heating pads, operation kits, vacuum formed trays, etc. Below are a few examples:
Thermoformed Trays:
-
Carts
-
Guards
-
Heating Pad
-
Blister Packs
-
Clamshells
-
Vacuum Formed Trays
-
Windshields
-
Skid Plates
-
Belly Pans
-
Hoods
Utility Vehicles
In addition to making products for cars, motorcycles, airplanes, buses, and boats, vacuum forming techniques are also used to manufacture windshields, guards, skid plates, belly pans, roofs, fenders, hoods, body panels, and covers for motorcycles, windshields, and consoles for snowmobiles, among other things. Furthermore, car companies can customize the shapes and colors of automobile parts through this process.
-
Fenders
-
Lawn Mower
Lawn and Garden Equipment
Vacuum forming is also used to make mower covers, guards, trailers, and fenders for lawn and garden equipment.
-
Guards and Trailers
-
Sign Holders
Packaging and Displays
Signs and billboards are also made using vacuum forming techniques in display centers. Acrylic is also used for mobile phone covers. Anything from food to electronic appliances can be packaged.
-
Trade Show Display
-
Custom Acrylic Display
-
Food Storage Containers
Plastic Food Containers and Trays
In the food and packaging industries, vacuum forming is widely used. Plastic trays and food storage containers, for example, are made from plastic, which is vacuum formed.
-
Plastic Trays
-
Plastic Packaging
-
Refrigerator Door Liners
Electronic Appliances
The vacuum forming process is widely used in panels, packaging, trays, and plastic boxes for appliances such as refrigerator parts, washing machine parts, vacuum cleaner covers, etc.
Chapter 4: The pros and cons of vacuum forming
Vacuum forming, like any method or technique, has its advantages and disadvantages. It is widely used because of its low cost and good productivity, but there are some cons to consider. The following are discussed:
Pros of Vacuum Forming
Affordability
Vacuum forming is more affordable than any other molding method. A low-cost molding process is more productive than a high-cost molding process. There are also affordable and readily available vacuum forming tools available.
Turnaround Time
Compared to injection molding, vacuum forming has a much longer turnaround time. Injection molding can be done in half the time with this process. By using 3D modeling, we can produce more products using vacuum forming in less time.
Flexibility
Using vacuum forming, manufacturers can experiment with new mold designs. It is possible to customize new models and colors to the molds, allowing clients to have more options according to their requirements at an affordable price.
Sterile and Food Grade Materials
For sterile and food-graded materials such as plastic food containers and medical equipment, vacuum forming is the best method. Vacuum-formed products are best since they can be sterilized and used for a long time and must be kept clean and germ-free.
Volume
Due to its scalability, vacuum forming is a rapid method. For mold formation, the tool is used one at a time, but a variety of devices can be used for different molds, thus creating a wide variety of products.
Consistency
The consistency of vacuum forming is well known. If we use the same mold for the same product, we will get the same results. It is possible to change the mold if the plastic is mishandled during mold formation.
Robustness
The robustness of vacuum forming is also well known. Some plastics are sensitive to others, but some are tough enough to withstand any resistance.
Cons of Vacuum Forming
One disadvantage of vacuum forming is that it is only feasible with plastics that have thin walls and consistency. Material walls that are thick and difficult to mold are unsuitable. Vacuum forming also has the disadvantage of being difficult to mold concave and deep parts of materials. Additionally, vacuum forming works well for small-scale production, but it isn’t suitable for large-scale production.
Conclusion
-
It is an ancient method of making plastic products using vacuum forming.
-
This is the simplest form of thermoforming, which uses vacuum suction pumps.
-
There are two types of molds: male molds and female molds.
-
The vacuum forming process involves the following steps. Plastic materials, clamping, heating, pre-stretching, plug assist, vacuum, cooling, trimming, and finishing.
-
The materials used for this process include polycarbonate, polyethylene, acrylic, PMMA, and PVC.
-
There are four types of vacuum forming machines. There are DIY machines, tabletop machines, single heater machines, and double heater machines.
-
Vacuum forming is widely used in medical, automotive, food packaging, and household products.
-
For small-scale production, vacuum forming is a good choice because it is flexible, time-saving, economical, and consistent.
-
Its limitation is the use of plastic for smaller-scale production and for thin-walled materials only.